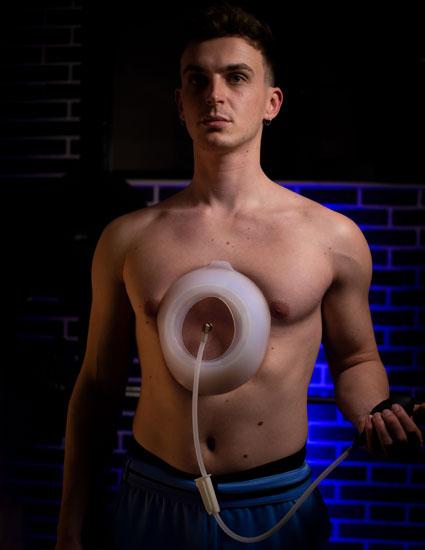
Sleep apnea can be one of the many possible breathing difficulties in people with pectus excavatum. It is a sleep disorder in which breathing stops and starts repeatedly.
You may have this disorder if you snore loudly and feel fatigued even after a long night's sleep.
APNEA LOWERS QUALITY OF LIFE
Aside from the cosmetic problem of the cavity, this abnormality can cause several health problems for the patient, depending on the severity of the deformity.
Organs, such as the heart and lungs, and vital functions in the human body might be disrupted and affected. Having those facts in mind, we understand that we can have a lower quality of life than the general population.
One of the essential things to function optimally during the day is having a good sleep. However, we are aware that difficulties such as sleep apnea might arise, even while sleeping, disrupting our resting quality. You shouldn't apply the vacuum bell while sleeping.
Quality sleep is a crucial factor in determining a person's overall happiness.
8 SYMPTOMS OF SLEEP APNEA
The following are some of the most prevalent signs and symptoms of sleep apnea:
- You may have loud and disturbing snoring.
- Sleeping episodes in which you stop breathing. Usually, someone else mentions this because it's often difficult to notice on your own.
- You may feel gasping for oxygen during sleep.
- A feeling of a dry mouth when waking up.
- Headache.
- Trouble sleeping (Insomnia)
- Excessive tiredness and sleepiness during the day (hypersomnia)
- Difficulties concentrating when awake.
CHEST DIFFICULTIES AND APNEA
Our chest might be affected by severe sleep apnea. As the pressure rises, the diaphragm and chest muscles work harder to open the airway during an apneic episode.
With a loud gasp or a bodily jolt, breathing generally continues. These episodes can disrupt sleep, limit oxygen delivery to essential organs, and cause abnormal heart rhythms.
PLEASE CONSULT WITH A DOCTOR
Because of these troubling apnea symptoms, it is crucial to be informed and see a doctor if it causes problems in doing your regular activities.
Because these two conditions have comparable symptoms, the symptomatology of apnea might frequently elicit the impression that it is our pectus excavatum. They are, nonetheless, closely related.
Please see a doctor if you have breaks in your regular breathing while sleeping. If you have breathing problems or wake up with shortness of breath, gasping, or choking, get medical help. These are all serious symptoms that you must treat on time.
EVIDENCE
There is a variety of evidence regarding the link between pectus excavatum and sleep-related respiratory issues, but it is still insufficient. Patients with difficulty breathing indicate that these are possibly caused by pectus excavatum.
Indeed, frequent increased intrathoracic negative pressure oscillations in people with sleep apnea may cause pectus excavatum. However, there is only minimal evidence for that occasion.
LARYNGOMALACIA
Laryngomalacia is another way of the possible connection between pectus and sleep apnea. A congenital weakening of the tissues of the larynx above the vocal cords is known as – laryngomalacia.
The most prevalent cause of loud breathing in somebody, especially youths, is this. The tissues fall across the airway opening and partially obstruct it because the laryngeal structure is deformed and flexible.
IS THIS DANGEROUS?
In most situations, laryngomalacia in people is not a dangerous problem. Due to the significant xiphoid retractions, some individuals with severe laryngomalacia may develop pectus excavatum and potentially chronic respiratory failure.
Even though adult laryngomalacia is rare, it may exist due to secondary trauma or surgery. Sleep quality is affected by pectus excavatum-related psychologic difficulties, particularly in individuals awaiting surgical correction.
It's an expected occasion because you are waiting for something significant to happen to you and your physique. Keep in mind that there are solutions for your sleeping problems and pectus excavatum.
POST-SURGICAL SLEEP QUALITY
Interestingly, sleep quality usually improves following pectus correction, most likely due to psychological improvement.
It's possible that once you've fixed what was causing you to lose your inner peace, you'll be able to sleep regularly again. Sleep apnea may go away after surgery.
BOTTOM LINE
Although sleep apnea with pectus excavatum seems complicated, there is an appropriate solution to overcome this. Early detection and treatment of any health problem is the best starting point.
But you must understand that it all starts and finishes with a healthy lifestyle. Live an active lifestyle and keep a healthy weight that does not aggravate your sleep apnea.
Apnea may disappear in some situations if you return to a healthy weight. Exercising is the best solution actually for sleep apnea.
Even without losing weight, regular exercise can help ease the symptoms of disturbing sleep apnea signs. Try to obtain at least 30 minutes of moderate activity throughout the day. Consistent walking can be enough sometimes.
Other than weight loss, another possible temporary solution can be changing the sleeping position. But, you still need to be aware that these natural remedies for apnea can help if the symptoms are mild.
8 Sources
- Sleep apnea - Symptoms and causes [Internet]. Mayo Clinic. [cited 2022 Dec 1].
Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sleep-apnea/symptoms-causes/syc-20377631 - Sleep Apnea: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment [Internet]. Cleveland
Clinic. [cited 2022 Dec 1]. Available from: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8718-sleep-apnea - Pectus excavatum is associated with sleep-related breathing disorders in children | European Respiratory Society [Internet]. [cited 2022 Dec 1]. Available
from: https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/54/4/1900524 - Laryngomalacia | Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia [Internet]. [cited 2022 Dec
1]. Available from: https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/laryngomalacia - The knowledge of paediatricians about laryngomalacia: is it always a trivial disease? [Internet]. [cited 2022 Dec 1]. Available from: http://pap.es/articulo.php?lang=en&id=12342&term1=
- Xiphoid Process: Pain, Lump, Removal, and More [Internet]. Healthline. 2017
[cited 2022 Dec 1]. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/health/xiphoidprocess - Surgical treatment of a case of adult epiglottic laryngomalacia - ScienceDirect
[Internet]. [cited 2022 Dec 1]. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1879729614000714 - pdf.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2022 Dec 1]. Available from: https://www.jtcvs.org/article/S0022-5223(18)32041-5/pdf